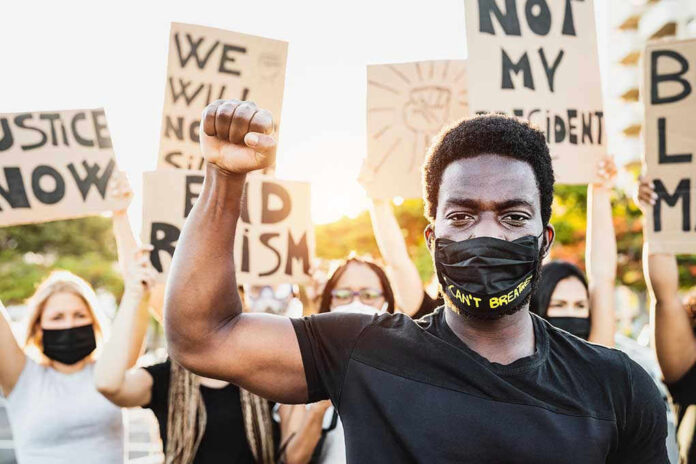
The reemergence of the Black Panther Party for Self-Defense in Philadelphia, armed and ready, has reignited debates about community protection versus federal authority.
Story Overview
- Black Panther Party’s armed presence at Philadelphia anti-ICE protest.
- Reaction to the fatal shooting of Renee Good by an ICE agent.
- Group claims continuity with the 1960s Black Panthers.
- Philadelphia’s resistance highlights local versus federal dynamics.
Armed Activism in Modern Context
The Black Panther Party for Self-Defense claims to be a modern iteration of the iconic 1960s group, known for its armed stance against systemic racism and police brutality. In Philadelphia, members legally carried military-style weapons during an anti-ICE protest following the fatal shooting of Renee Good by an ICE agent in Minneapolis. The group’s leadership, particularly Paul Birdsong, issued strong warnings to federal agents, positioning themselves as protectors of the community. This act has sparked a significant national conversation on the role of armed activism today.
The group’s appearance at the protest, armed yet legally justified under local open carry laws, underscores the tension between federal immigration enforcement and community self-defense strategies. Philadelphia, a sanctuary city, has long been at odds with federal immigration policies. District Attorney Larry Krasner has been vocal in his opposition, threatening prosecution for any federal overreach. This backdrop sets the stage for the Black Panther Party’s resurgence, raising questions about the balance between legal rights and community safety.
Historical Echoes and New Dynamics
The contemporary Black Panther Party identifies itself with the original party’s legacy, founded by Huey P. Newton and Bobby Seale. However, today’s group describes itself as more aggressive, reflecting the heightened tensions of the current political climate. The fatal shooting of Renee Good galvanized the group into action, serving as a catalyst for their armed mobilization. The protest in Philadelphia not only revived historical images of the 1960s but also highlighted the evolving nature of community activism in response to federal actions.
While the group asserts its continuity with the past, there are questions about the official recognition of this modern iteration. Despite this, their presence and rhetoric have undeniably influenced the protest landscape. Video footage of confrontations between the Black Panther members and ICE agents has spread nationally, drawing widespread attention and prompting debates on protest tactics and federal enforcement consistency.
Local Resistance and National Implications
Philadelphia’s stance against ICE operations, supported by local authorities like Krasner, has positioned the city at the forefront of a broader resistance movement. The Black Panther Party’s involvement adds an armed dimension to this resistance, challenging federal agents with their visible and vocal presence. The group’s strategy includes not only protest appearances but also advocating for community members to escort immigrants, aiming to shield them from ICE enforcement.
This armed mobilization raises critical legal and constitutional questions about open carry rights, community self-defense, and the boundaries of legal activism. The incident has not only captured national media attention but also sparked debates about the effectiveness and ethics of such protest strategies. As the group plans sustained demonstrations, the potential for escalation or broader replication in other jurisdictions looms large, posing significant implications for federal-local relations and immigration enforcement practices.



















